 |
|
|
Internship at the Marion State
Fish Hatchery |
|
Written by: Ashley Upton, Biology
Major |
| |
 |
Marion State Fish Hatchery is the largest of three
freshwater fish hatcheries located in the state of Alabama. These hatcheries
are affiliated with the fisheries section of the Alabama Department of Wildlife
and Freshwater Fisheries. Each hatchery focuses on producing fish and stocking
waterways throughout the state of Alabama. Marion Hatchery has five main
purposes: receiving broodstock, spawning fish, producing fry, harvesting ponds,
and stocking waterways throughout the state. |
|
| |
|
| Marion Hatchery begins receiving striped bass
broodstock in March. Most of the striped bass broodstock are received from
Lewis Smith Lake and the Coosa River. Upon arrival at the hatchery, each fish
is weighed and placed under anesthesia using MS-222 to reduce the stress
administered during handling. Each fish is also tagged for identification
purposes. |
 |
| |
|
|
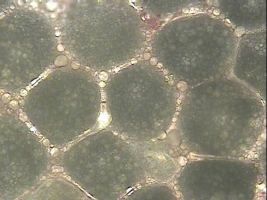 |
| |
The picture
above shows typical stage
one
eggs. |
|
The eggs
of female striped bass must be staged to determine the time until the fish will
spawn. Eggs are abstracted by inserting a glass catheter through the genital
pore into the ovaries. The eggs are then viewed under a microscope to determine
the amount of time until the fish will ovulate. |
| |
|
 |
 |
|
| |
| If the eggs are at a stage
one, the female striped bass is injected with Luteinizing Hormone Releasing
Hormone (LhRh) to speed up the ovulation time. If needed, the fish will later
be injected with Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG). All of the female
broodstock are injected with one or both of the hormones in order to speed up
ovulation time and to ensure that the time until the fish will spawn is
predictable to the staff of the hatchery. Males can also be injected with the
hormones to induce milt production. |
| |
 |
 |
| |
|
| Upon ovulation, the eggs
will flow freely from the female indicating that it is time to spawn. Eggs are
fertilized with the milt from many striped bass males to ensure genetic
diversity. White bass males can be used in the spawning process if hybrids are
desired. The eggs and milt are mixed with water using a feather. Little
pressure is exerted during the mixing process to ensure that the eggs are
fertilized without causing damage to them. This is a very precise process
considering sperm motility lasts only 30 to 60 seconds and eggs remain fertile
for only two minutes after added to water. |
| |
|
 |
|
| |
|
| After spawning is complete, the
fertilized eggs are equally apportioned into hatching jars. Each hatching jar
is subject to constant water circulation to ensure that the eggs do not settle
to the bottom and suffocate. After the eggs hatch, the fry are placed in
troughs where their swim bladders inflate allowing them to develop swimming
skills. While in the troughs, fry feed off of their yolk sac until about day
five when their mouth parts develop allowing them to consume brine shrimp. |
 |
| |
|
 |
When the fry reach a
couple of millimeters in length, they are stocked into ponds at the hatchery.
Marion Hatchery has over 30 ponds. While in the ponds the fry feed off of
zooplankton, which are stocked into these ponds by the hatchery personnel.
|
| |
|
| When the fry reach an inch
or so in length, they are considered fingerlings and are the proper size to be
harvested. When the fingerlings are ready to come out of the ponds, they will
begin swimming around the banks of the ponds. When this occurs, the ponds are
drained and the fingerlings are gathered using nets and then placed in vats
until time for shipping. |
 |
| |
|
| Each
year, fisheries biologists visit waterways throughout the state to evaluate
fish populations. Any inadequacies are relayed to hatcheries where needed fish
are produced and stocked into these lakes and rivers to prevent population
decreases. When fingerlings arrive at the stocking location, they are first
acclimated to the receiving waters. This is especially important if the
temperature difference between the hauling water and receiving water is greater
than 2ºF. After the fingerlings are acclimated, the drain of the hauling
basin is opened and the fish are allowed to swim through the drain into the
receiving waters. After the striped bass fingerlings are stocked, the long
process of capturing broodstock and later stocking tens of thousands of
fingerlings in its place is completed. |
| |
|
 |
 |
|
|
| |
 Webspinner Table of Contents Webspinner Table of Contents |
|